压铸模具PVD涂层解决方案

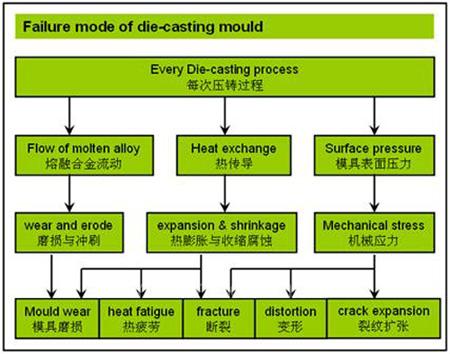
Problems: The primary stress to which the surface of the mould is exposed are thermal shock, abrasion and chemical reactions between the liquid alloy and the iron in the steel mould. Certain regions of the mould are subjected to especially high stresses. In particular, these include ribs and the near-gate sections, where abrasion occurs owing to the high velocity of the molten alloy.
问题:压铸模具表面主要面临的问题有热冲击、磨损、液态合金与模具钢的化学反应等。某些地方还有高应力,特别是成型筋的部位和浇口部位,这些地方由于高速熔融合金流动易发生磨损。
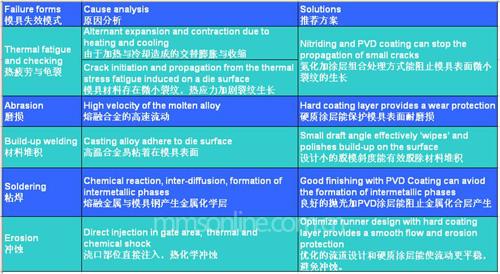
Solutions 解决方案:
Materials selection: requires high temperature strength, toughness, hardness, and wear resistance.
钢材选择:需兼具高温强度,高韧度,高温硬度和抗磨损;
Design: adopt small draft angle to reduce soldering, avoid sharp corner to reduce crack ,optimize runner system to reduce erosion.
模具设计:选用小的脱模角度减少粘焊,避免尖角应力造成开裂,优化流道设计减少冲蚀。
Nitriding and oxidation: diffusion layer and oxidation layer improve soldering resistance, adhesion resistance and crack resistance.
氮化扩散层和氧化层:可以提高模具耐溶损性、耐过烧性、耐粘着性和耐热裂性。
Maxit® Coating: Ensuring Max. service temperature of PVD hard layer exceeds the molten alloy.
Maxit®涂层:选用合适的涂层以避免高温失效。
声明:本网站所收集的部分公开资料来源于互联网,转载的目的在于传递更多信息及用于网络分享,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,也不构成任何其他建议。本站部分作品是由网友自主投稿和发布、编辑整理上传,对此类作品本站仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如果您发现网站上所用视频、图片、文字如涉及作品版权问题,请第一时间告知,我们将根据您提供的证明材料确认版权并按国家标准支付稿酬或立即删除内容,以保证您的权益!联系电话:010-58612588 或 Email:editor@mmsonline.com.cn。

- 暂无反馈
